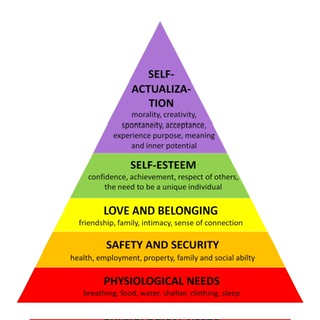
Abraham Maslow (1943, 1954) says human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, from survival needs to self-actualization’ at the top.
- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs, often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid.
- The five levels of the hierarchy are physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization.
- Lower-level basic needs like food, water, and safety must be met first before higher needs can be fulfilled.
- Few people are believed to reach the level of self-actualization, but we can all have moments of peak experiences.
- The order of the levels is not completely fixed. For some, esteem outweighs love, while others may self-actualize despite poverty. Our behaviors are usually motivated by multiple needs simultaneously.
- Applications include workplace motivation, education, counseling, and nursing.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory of motivation which states that five categories of human needs dictate an individual's behavior. Those needs are physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs
Links